C-Peptide
Specimen Volume
1mL bloodTurnaround Time
7 daysSample Stability
RT stability: 24 hours, 2-8C: 2 days off cells; -20C 3 monthsGeneral Information
Determination of the C-peptide is an additional option to monitor average β-cell insulin secretion. C-peptide is used as a test of β-cell function in a variety of conditions including type 1 diabetes, and to aid in the differential diagnosis of hypoglycemia, and surreptitious insulin self-administration. A low C-peptide level is expected if the insulin secretion is diminished as in insulin-dependent diabetes (type 1 diabetes, latent autoimmune diabetes of adults (LADA)). Elevated C-peptide levels may be found when β-cell activity is increased as in hyperinsulinism, insulin resistance (with high blood glucose) and insulinomas (with low blood glucose). Inappropriately raised plasma insulin concentrations in the presence of low or suppressed plasma C-peptide will identify patients with exogenous insulin administration. Suppressed plasma insulin and C-peptide concentrations in the presence of hypoglycaemia can be caused by chronic kidney disease, liver disease, alcohol and drugs.
C-peptide is cleared by the kidneys, therefore impairment in renal function can make C-peptide results difficult to interpret.
Patient Preparation
If using for investigation of hypoglycaemia, patient must be hypoglycaemic at time of sampling (Venous glucose = <4.0 mmol/L).
Notes
Cannot analyse haemolysed samples.
Needs separate EDTA for C-peptide if simultaneous HbA1c/FBC is requested.
A paired glucose sample is required to allow for correct interpretation.
Reference Range
Diagnosis of diabetes
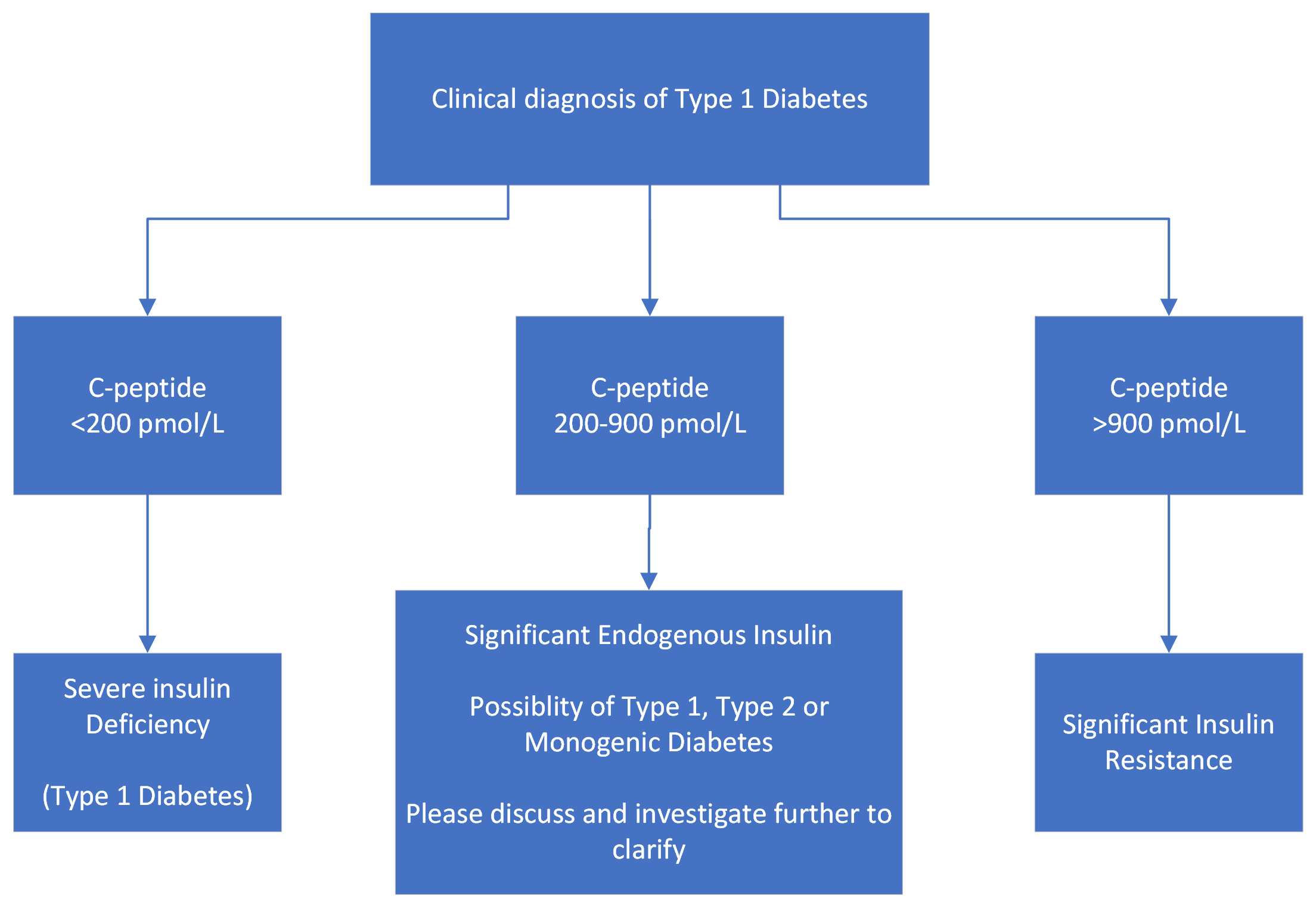
Non- diabetic hypoglycaemia
See QEHB Pathology Departments - Insulin
Specifications
- EQA Status: UK NEQAS Guildford Peptide Hormones
- EQAS Scheme: Yes